ECS gives us insight in how our body truly works
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) was identified in the 1990s by researchers who were trying to explore the effects of THC. Since then, the ECS has become a topic of heavy research – mainly because it is through this system that cannabis interacts with our bodies.
Whatever health benefits that we know of when it comes to cannabis – whether it is THC or CBD – it all happens via the endocannabinoid system.
A better understanding of it is the key to unlocking more ways in which cannabis can positively influence our lives.
This article will tell you all there is to know about the ECS in a simple, easy-to-understand manner.
What is the endocannabinoid system?
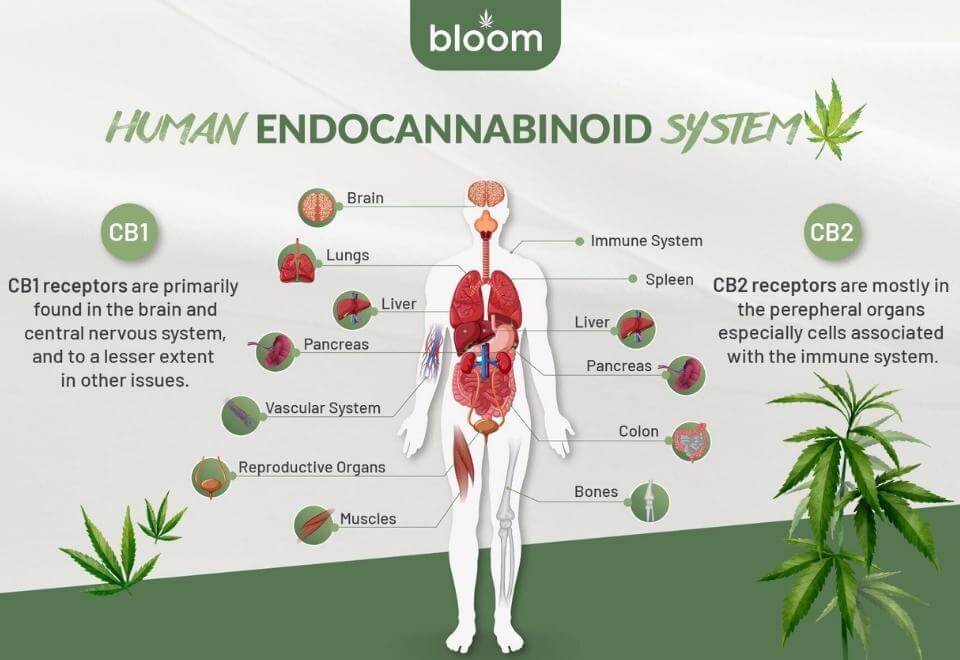
The ECS is a biological, cell-signalling system that regulates several processes in our bodies like sleep, memory, pain, inflammation, immunity, reproductive health, appetite, etc. It is present everywhere and is important to our survival.
There are three elements to this system:
Endocannabinoids
These are cannabinoids produced by our body as and when needed. The term ‘endo’ means ‘within.’ These are basically neurotransmitters that send chemical messages between nerve cells in our bodies.
Endocannabinoids have a similar structure to the cannabinoids found in cannabis plants. It is for this reason why cannabis and marijuana can affect us so greatly.
These molecules help with several bodily functions and ensure that they run smoothly. At the moment, scientists have identified two endocannabinoids:
- Anandamide: Derived from the Sanskrit word ‘ananda,’ which means ‘joy, bliss.’ It is also known as the “happy molecule” and is believed to manage pain response. The feeling is quite similar to eating chocolate after a craving.
- 2-arachidonoylglyerol (2-AG): It is the most common endocannabinoid in our body and is mainly involved with anti-inflammatory function.
Endocannabinoid receptors
Endocannabinoids do their magic by binding with the specialised receptors placed all through the body. When cannabinoids attach to these receptors, a signal is sent to the ECS to take the necessary action.
There are two main endocannabinoids receptors:
- CB1: This is present primarily in our central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord.
- CB2: This is present in the peripheral nervous system, including limbs, organs, and immune cells.
Endocannabinoids can attach themselves to either of these receptors. The end result of that depends on the location of the receptor and which endocannabinoid it is binding itself to.
Enzymes
Enzymes are responsible for producing and breaking down endocannabinoids after they have done their job. There are two primary enzymes involved in this process:
- Fatty acid amide hydrolase, which breaks down Anandamide
- Monoacylglycerol acid lipase, which breaks down 2-AG
How does the endocannabinoid system work?
Our body naturally produces endocannabinoids as and when needed. They are present throughout and become active only when they bind to a receptor.
The exact know-how of its workings is something that is still being researched. However, it is understood that when the body is out of balance or its internal stability is disturbed, the ECS comes into the picture to fix the problem.
For example, if your body temperature rises due to an external problem like injury, stress, etc., the ECS kicks in and works hard to return your body to its ideal state (homeostasis). Similarly, the ECS, mainly via the CB2 receptors, manages the response when your body is in pain.
Functions of the endocannabinoid system
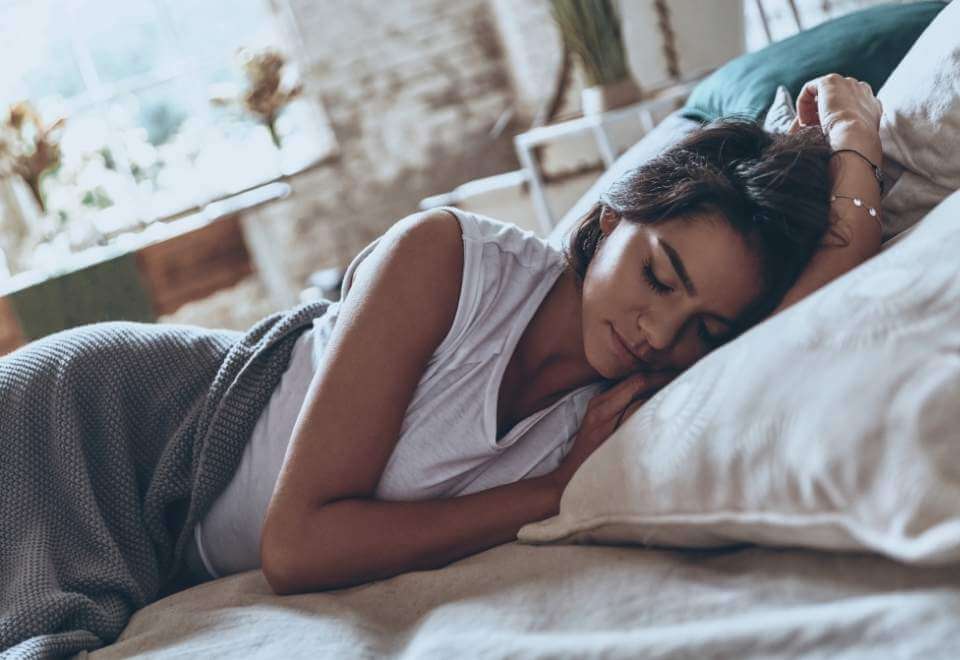

The primary function of ECS is to maintain the state of homeostasis in our bodies. Homeostasis refers to internal stability achieved after an injury or if you get sick.
Homeostasis is a steady state of equilibrium in our body by balancing the millions of biological and chemical processes.
ECS basically acts as a master regulator and allows us to stay at homeostasis. Think of ECS as the autopilot and your body as the plane. Whenever turbulence occurs, autopilot steps up and ensures a smooth journey without any disturbances.
The endocannabinoid system is involved in regulating functions like:
- Sleep & mood
- Pain response & inflammation
- Immune function & temperature regulation
- Reproductive functions
- Metabolism, appetite & digestion
- Stress response
- Memory and learning
Cannabinoids and ECS: How can taking cannabis help you?

Cannabis plants have over 100+ cannabinoids, but only two are of interest to us: THC and CBD.
THC can “take over our body” by attaching to the CB1 and CB2 receptors. Since CB1 receptors are present in the spinal cord and brain, you feel the ‘high’ sensation accompanied by laughter, happiness, paranoia, slow perception of time, poor memory, etc. At the same time, THC can also help with managing pain, inducing sleep and appetite, treating nausea and vomiting associated with chemotherapy, etc.
On the other hand, CBD does not get you high and is not associated with the negative effects of THC. It is not known how CBD interacts with the endocannabinoid system, but it is known that it does not bind to the receptors like THC.
Instead, it is believed that CBD prevents the breakdown of endocannabinoids, allowing them to flow more freely in our bodies.
Case in point, CBD prevents Anandamide from being synthesised by enzymes, therefore increasing the levels of this bliss molecule in our system. As a result, we feel calm and relaxed – one of the known positive factors of CBD.
Parting thoughts

The endocannabinoid system is crucial to our survival. Without it, our internal stability would be lost and we would be highly sensitive to every external change. Not only this but the ECS is also involved in regulating various important functions in our bodies.
Scientists are still studying the ECS, and there is a lot we don’t know about it. However, knowing it better can lead to treating many health conditions.
Theoretically, you can take cannabis to help your ECS system do its job better. We recommend CBD products such as oil with CBD since it will not get you high and allow you to experience the full benefits of cannabis plants.









 @bloom.asia
@bloom.asia







