When it comes to cannabis, terpenes and weed go hand in hand. Without terpenes, there is no weed – these aromatic compounds play a crucial role in your cannabis experience. For example, if you smoke two different buds with the same THC concentration, your ‘trip’ or the high will differ. This is quite likely due to the terpenes present in the two flowers.
So, what are terpenes? How do they work? Do they have any psychoactive effects? This article addresses the fundamental questions surrounding cannabis terpenes – read on to see why these compounds matter and how knowing about them can help you refine your marijuana experience.
Cannabis Terpenes 101
The scent of weed is unmistakable – you will most likely smell it before you see it. That skunky, pungent, or intensely fruity smell indicates the presence of fresh mary jane nearby. For non-weed enthusiasts, the smell of pine cones, lavender, or herbs and the new summer scent of mangoes are all due to terpenes.
What are terpenes
Terpenes are aromatic compounds responsible for the various flavours, colours and pigmentation, and unique scents of plants. All plants naturally produce terpenes as they are vital to survival; they are found throughout the plant kingdoms in almost every flower – over 20,000 terpenes have been identified.
In the context of cannabis, terpenes serve the same purpose. For example, the citrusy scent from your Lemon Haze strain is likely due to limonene. In contrast, an earthy, fruity smell in the 10th Planet R1 strain comes from myrcene.
Terpenes are found in the trichomes of female cannabis plants. Trichomes are nothing but shiny, white, sticky hair-like substances found on the buds, flowers, and leaves of marijuana plants. They are the resin glands of the plant, which give the frosty appearance.
Their purpose in nature
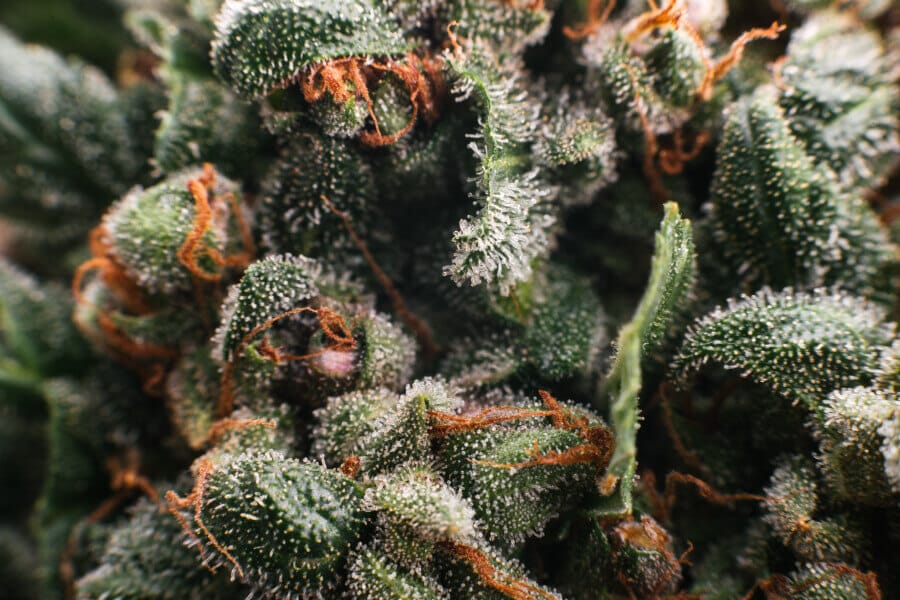

Terpenes can be considered secondary compounds produced by plants to help facilitate their growth, reproduction, and survival. In other words, terpenes help plants:
- Attract pollinators by making the plant seem more appealing
- Repel predators by either targeting the predator’s reproductive system (thus keeping them away from the plan), being toxic to the creature or attracting other helping insects or allies that feed on these harmful predators
- Combat infection; many terpenes carry antimicrobial and antifungal properties that help the plants boost their immune system and thus ensure their survival
- Act as sunblock; certain terpenes can also shield the plant from harsh UV rays in case of the excess sunlight
At the moment, scientists have identified over 150 cannabis terpenes. Still, a vast majority of them are in trace amounts (very small amounts) – so much so that they do not require a lot of research. However, a few of them, like limonene, myrcene, caryophyllene, limonene, and pinene, are of great interest to weed growers and users.
How do Cannabis Terpenes Interact with the Body?
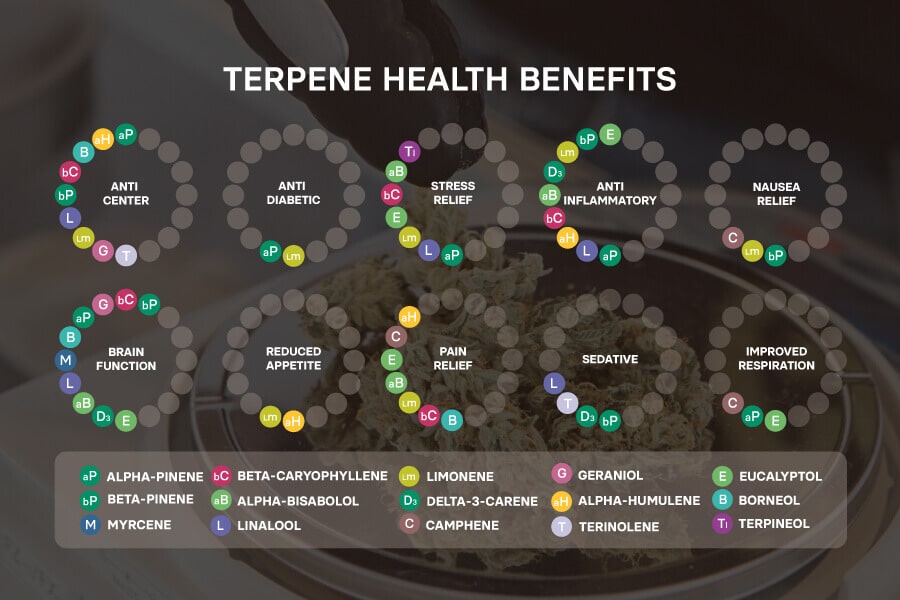
Overall, terpenes contribute to the chemical profile or makeup of the strains in the weed industry – which is becoming more critical by the day. This is because terpenes have been shown to interact with the human body – and some scientific research validates the therapeutic use of terpenes.
For example, limonene has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that make it a viable candidate for treating various health conditions. Similarly, myrcene is another well-known terpene famous for its anti-anxiety, sedative, analgesic, and antioxidant properties. Early studies indicate it may reduce inflammation and pain.
This is also in line with why myrcene-rich weed strains OG Kush or Granddaddy Purple make you sleepy and relaxed. Myrcene is also a vital part of aromatherapy, comprising a significant portion of essential oils.
What happens when you consume terpenes
Coming to cannabis, the link between terpenes and cannabinoids like THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) can be explained via the entourage effect.
Before we proceed further, there are a few things you must remember:
- Terpenes by themselves will not get you high or intoxicated. They can have certain effects on your body, as seen above
- Terpenes are not the same as cannabinoids; they are a different class of compounds altogether that does not bind directly to the receptors in the endocannabinoid system
So, how do terpenes work, then?
The answer is simple – they work synergistically with cannabis compounds. The idea here is simple – the effect of cannabis on the human body when consumed as a whole with all its compounds – cannabinoids and terpenes – is far greater than when consumed by themselves.
For example, a thorough scientific review of the entourage effect shows that terpenes coupled with cannabinoids can be useful in treating mood and anxiety disorders. Similarly, a 2010 study showed that THC and CBD, when used together, are more effective in reducing pain than THC alone.
In short, it is a complementary relationship where terpenes work together with THC, CBD, and all their cousins to enhance your experience. This does stand to reason, considering what we know about individual terpenes and their effects. For example, a limonene or pinene-rich strain can make you giggly and happy – which is harmonious with the fact that limonene is a known mood-uplifting compound.
Another way to look at this is as follows:
If compounds like CBD and THC, and their concentration, comprise the car’s engine, then terpenes act as the driver behind the steering wheel. The cannabinoids will power your engine and give you a good boost, while terpenes will guide you on your trip. Depending on the terpene profile of your bud, you will have a different kind of experience.
Common Cannabis Terpenes

Myrcene
The Mother of all Terpenes, myrcene is the most common terpene found in cannabis plants. It has an earthy, herbal scent, known for its sedative and sleep-aid effects. It is also found in mangoes, thus giving rise to the notion that eating a mango before consuming cannabis can increase your high.
Limonene
Limonene is highly aromatic and pungent, giving a strong citrusy aroma. It has stress-relief and anti-depressant properties and is associated with energising and uplifting your mood.
Pinene
Another well-known terpene, pinene has an aromatic profile similar to pine cones or pine forests. It is known for its mood-elevating effects and can help improve focus, alertness, and even memory loss associated with THC.
B-Caryophyllene
Also known as beta-caryophyllene, it has a characteristic pungent, spicy, peppery scent. In addition to cannabis, it is found in black pepper, cloves, and cinnamon. Studies have shown caryophyllene has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-depressant properties.
Linalool
Linalool is an abundant terpene with an unmistakable smell of lavender, thus giving a floral scent. It is a well-known sedative that can help reduce anxiety and depression, alongside providing other health benefits.
Parting Thoughts
Even though we know a fair bit about terpenes, there is a whole lot we do not understand. The research is still growing, especially regarding their interaction with the human body. But one thing is clear – terpenes have a clear potential to elevate our cannabis experience. Weed growers must consider this into the equation when cultivating different marijuana strains – while weed stores in Thailand should strive to point out the terpene profile on each of their offerings.
As a user, you may also want to consider how different terpenes affect your high and the kind of effects they cause. For example, a myrcene-rich strain can help you relax after a long day at work, while a limonene-rich flower can energise you and give you the mental clarity to complete the task. Therefore, looking at the test results and packaging labels is one way to do this.
Similarly, you can use your nose to identify what terpene is dominant in the bud. Again, this will take time and practice, but soon, you will be able to point out the leading terpene in the strain and decide whether it is suitable for you at the moment.
All in all, terpenes are the new craze in the cannabis industry, and they are here to stay.










