Cannabis has become more integrated into the daily lives of Thai people since changes to cannabis laws were announced, allowing for its use in medical contexts. Cannabis contains a variety of compounds that are increasingly recognized for their ability to provide various benefits to the body. One of the more interesting and commonly known compounds in marijuana is THC, which is responsible for the “high” associated with cannabis use. Due to its psychoactive effects, this substance has been the subject of controversy and has been illegal in many countries, including Thailand, for an extended period of time.
What is THC? and What is Its Chemical Composition?
THC stands for delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol, which is a psychoactive compound found in the cannabis plant. It is the primary psychoactive ingredient in marijuana and is responsible for the “high” that is commonly associated with the use of this drug.
THC Structure and Properties: How It Interacts with the Body
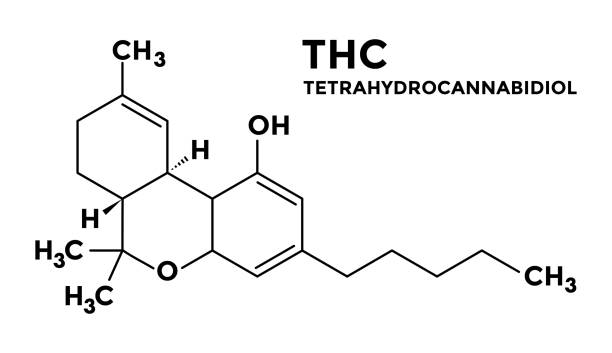
Chemically, THC is a cannabinoid, a class of compounds that interact with receptors in the brain and body that make up the endocannabinoid system. THC has a molecular formula of C21H30O2 and a molecular weight of 314.46 g/mol.
The chemical structure of THC is characterized by a cyclohexene ring with a double bond and a side chain with a methyl group at the third carbon atom. This structure is responsible for its ability to bind to specific receptors in the brain and produce its psychoactive effects.
THC content in cannabis can vary depending on the strain, growing conditions, and processing methods, but in general, the concentration of THC in marijuana can range from 5-30%.
The Differences Between THC and Other Cannabinoids, and Their Respective Benefits and Effects.
THC is just one of over 100 cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. Each cannabinoid has unique effects and potential benefits. Here are some of the differences between THC and other cannabinoids, including CBD, CBN, and CBG:
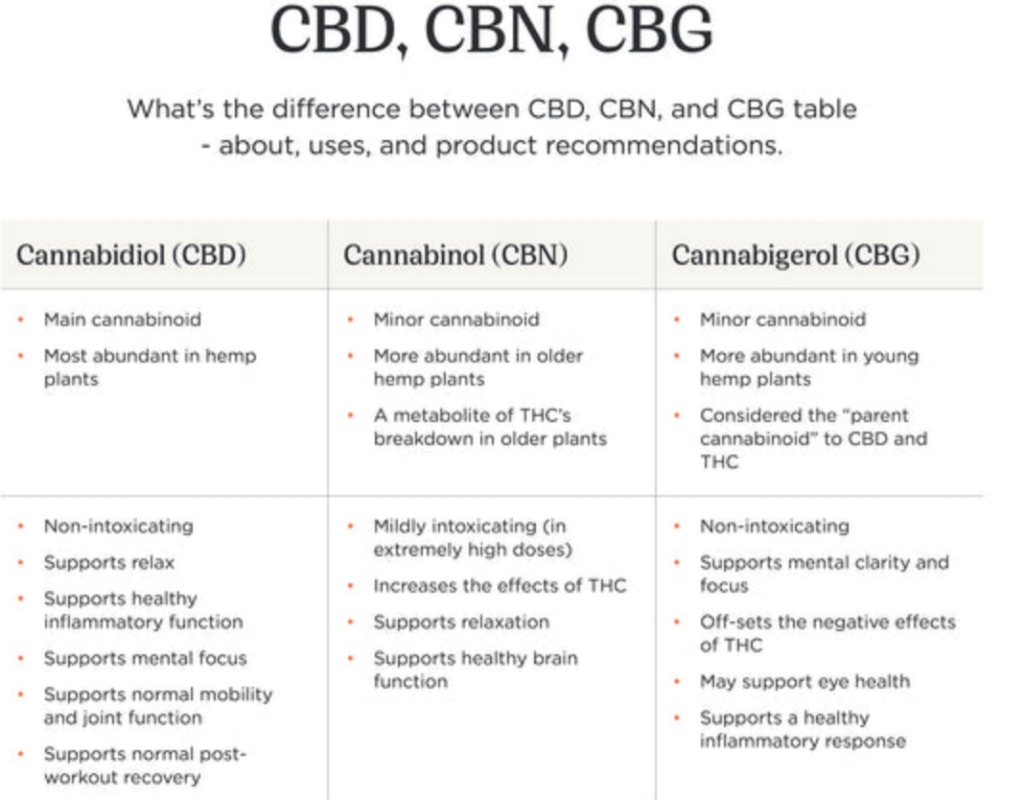
- CBD: CBD (cannabidiol) is non-psychoactive, which means it does not produce a “high.” Instead, it is thought to have a range of potential therapeutic benefits, such as reducing inflammation, anxiety, and seizures. CBD has also been shown to modulate the effects of THC, potentially reducing its negative side effects.
- CBN: CBN (cannabinol) is a cannabinoid that is produced when THC oxidizes over time. It is thought to have sedative effects and potential benefits for insomnia, pain relief, and inflammation.
- CBG: CBG (cannabigerol) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid that is thought to have potential benefits for reducing inflammation, anxiety, and pain. It may also have antibacterial properties and could be useful for treating conditions such as Crohn’s disease and glaucoma.
How THC Interacts with the Body’s Endocannabinoid System
THC interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system primarily by binding to and activating specific receptors in the brain and body that make up this system. The endocannabinoid system is a complex network of receptors, enzymes, and endocannabinoids (cannabinoids produced by the body) that is involved in regulating a variety of physiological processes, including mood, appetite, pain sensation, inflammation, and immune function.
Endocannabinoid Receptors and Signaling Pathways
The two primary cannabinoid receptors in the endocannabinoid system are CB1 and CB2 receptors. CB1 receptors are primarily found in the brain and central nervous system, while CB2 receptors are primarily found in immune cells and peripheral tissues.
- CB1 receptors are primarily found in the central nervous system, where they play a key role in regulating neurotransmitter release and synaptic plasticity. When activated by endocannabinoids or phytocannabinoids like THC, CB1 receptors inhibit the release of neurotransmitters such as glutamate, GABA, and dopamine, leading to a range of effects on mood, cognition, and motor function.
- CB2 receptors are primarily found in immune cells and peripheral tissues, where they play a role in modulating inflammation and immune function. When activated by endocannabinoids or phytocannabinoids, CB2 receptors can help to reduce inflammation and immune cell activation, potentially offering therapeutic benefits for conditions such as autoimmune disorders and chronic pain.
When THC enters the body, it binds to CB1 receptors in the brain and activates them, producing a range of psychoactive effects, such as changes in mood, perception, and appetite. THC also has the potential to modulate other neurotransmitter systems in the brain, such as the dopamine and serotonin systems, which can further contribute to its effects.
In addition to its effects on CB1 receptors, THC can also bind to CB2 receptors, which are primarily involved in regulating immune function and inflammation. This interaction with CB2 receptors may contribute to THC’s potential anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
The Health Benefits of THC: How It Can Improve Your Quality of Life

THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is a psychoactive cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant that has been shown to offer a range of potential health benefits.
Pain Management: How THC Can Help with Chronic Pain
THC has been shown to be effective in reducing chronic pain, making it a potential treatment option for individuals with conditions such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, and neuropathic pain. THC works by interacting with the endocannabinoid system and other signaling pathways in the body to reduce inflammation and modulate pain signals. It may also enhance the pain-relieving effects of other cannabinoids, such as CBD.
While THC can be an effective pain reliever, it is important to note that it can also produce side effects such as dizziness, sedation, and impaired cognitive function. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before using THC or any other cannabinoid for pain management, and to use it responsibly and in accordance with local laws and regulations.
Appetite Stimulation: How THC Can Help with Weight Loss and Eating Disorders
THC has been shown to stimulate appetite, making it a potential treatment option for individuals with conditions that cause loss of appetite or weight loss, such as HIV/AIDS or cancer. THC works by interacting with the endocannabinoid system and other signaling pathways in the body to increase hunger and food intake. It may also enhance the pleasure and reward response associated with eating, making it more enjoyable for individuals with eating disorders such as anorexia or bulimia.
However, it is important to note that THC can also produce negative side effects such as increased heart rate and anxiety, particularly at high doses. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before using THC or any other cannabinoid for appetite stimulation, and to use it responsibly and in accordance with local laws and regulations.
Reducing Anxiety and Depression: The Benefits of THC for Mental Health
THC has been shown to have mood-enhancing effects, making it a potential treatment option for individuals with anxiety and depression. THC works by interacting with the endocannabinoid system and other signaling pathways in the body to increase the availability of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, which are involved in regulating mood and emotion. It may also reduce anxiety by reducing activity in the amygdala, a part of the brain that is involved in fear and anxiety responses.
However, it is important to note that THC can also produce negative side effects such as increased heart rate, paranoia, and impaired cognitive function, particularly at high doses. It is important to consult with a healthcare provider before using THC or any other cannabinoid for anxiety or depression, and to use it responsibly and in accordance with local laws and regulations.
The Use of THC in Creative and Artistic Pursuits: How It Can Affect Creativity and Inspiration.
THC has been associated with enhancing creativity and inspiration among artists, musicians, writers, and other creative professionals. Many people report that THC use can help them enter a state of flow where ideas and thoughts flow freely, leading to more original and innovative work. THC is also known to enhance sensory perception, which can lead to new perspectives and insights into familiar subjects.
However, the effects of THC on creativity can vary widely depending on the individual and the dosage. High doses of THC can impair cognitive function, leading to confusion, memory loss, and reduced creativity. Furthermore, long-term THC use may cause tolerance, which can decrease its effects on creativity over time. Overall, while THC may have the potential to enhance creativity and inspiration, it is important to use it safely and responsibly to avoid negative side effects.
The Risks and Side Effects of THC Use: What You Need to Know

While THC can have potential health benefits, it is important to be aware of its risks and side effects. Additionally, THC can be addictive for some individuals and may lead to withdrawal symptoms when use is discontinued. Here are some of the risks and the side effects of using THC.
Short-Term Side Effects of THC Use: Dry Mouth, Red Eyes, and Impaired Coordination
Some of the most commonly reported short-term side effects of THC use include dry mouth, red eyes, and impaired coordination. Dry mouth, or “cottonmouth,” occurs when THC interacts with the salivary glands, leading to a reduction in saliva production. This can cause a dry or sticky feeling in the mouth and throat, as well as increased thirst.
Red eyes occur when THC dilates the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to increased blood flow and a reddish appearance. Impaired coordination can also occur due to THC’s effects on the brain and nervous system, leading to reduced balance and coordination, and an increased risk of accidents or falls.
While these side effects are generally mild and temporary, they can be uncomfortable or inconvenient for some users. Drinking water, using eye drops, and avoiding activities that require coordination or fine motor skills may help to alleviate these side effects.
Long-Term Risks of Heavy THC Use: Respiratory Problems, Addiction, and Mental Health Issues
While the short-term side effects of THC use are generally mild and temporary, long-term heavy use of THC can increase the risk of certain health problems. One of the most significant risks is respiratory problems, as smoking or inhaling THC can cause lung damage and increase the risk of lung infections and other respiratory issues. Additionally, long-term THC use can lead to addiction in some individuals, with withdrawal symptoms such as irritability, insomnia, and loss of appetite when use is discontinued.
Long-term THC use has also been associated with an increased risk of mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and psychosis, particularly in individuals who are predisposed to these conditions. It is important to use THC responsibly and in accordance with local laws and regulations, and to consult with a healthcare provider if you have concerns about your THC use or its potential health effects.
The Potential Risks of THC Use During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding.
THC use during pregnancy and breastfeeding is a particularly sensitive issue, as THC can cross the placenta and be transferred to the fetus or the breast milk. The use of THC during pregnancy has been associated with an increased risk of low birth weight, preterm labor, and developmental problems in the fetus. Additionally, THC use during breastfeeding can lead to THC exposure in the infant, which can affect brain development and lead to impaired cognitive function and behavior problems later in life.
It is recommended that pregnant and breastfeeding individuals avoid THC use, and that those who use THC for medical reasons consult with a healthcare provider to explore alternative treatment options. It is important to prioritize the health and well-being of both the mother and the infant, and to be aware of the potential risks of THC use during this critical period of development.
The Impact of THC Use on Driving and Safety.
The impact of THC use on driving and safety is a major concern, as THC can impair driving ability and increase the risk of accidents. THC use can cause dizziness, impaired coordination, slowed reaction times, and altered perception of time and distance, all of which can make it difficult to safely operate a vehicle. Additionally, THC can impair judgment and decision-making abilities, leading to risky or reckless behavior on the road.
Studies have shown that driving under the influence of THC increases the risk of accidents, particularly for inexperienced or young drivers. It is important to avoid driving or operating heavy machinery while under the influence of THC, and to be aware of local laws and regulations regarding THC use and driving. Additionally, individuals who use THC should be mindful of its potential effects on coordination and judgment, and avoid activities that require fine motor skills or mental alertness until the effects of THC wear off.
How to Use THC Safely and Responsibly: Dosage, Frequency, and Setting
Using THC safely and responsibly involves a variety of factors, including dosage, frequency, and setting. When using THC, it is important to start with a low dose and gradually increase as needed, as THC can have different effects on different individuals. It is also important to avoid overusing or using THC too frequently, as this can increase the risk of developing tolerance, dependence, or other negative health effects.
The setting in which THC is used can also play a role in its effects, as using THC in a safe and comfortable environment with trusted friends or loved ones can help to reduce the risk of anxiety or other negative experiences.
Additionally, it is important to be aware of the legal and regulatory status of THC in your area, and to use it in accordance with local laws and regulations. Consulting with a healthcare provider or qualified cannabis specialist can also help to ensure safe and responsible THC use, and can provide guidance on dosage, frequency, and other important factors.
Tips for Safe and Effective THC Use
Here are some tips for safe and effective THC use in bullet point form:
- Choose a trusted and reliable source of THC, such as a licensed dispensary or reputable online supplier
- Start with a low dose and gradually increase as needed, rather than consuming a large amount all at once
- Avoid mixing THC with other substances such as alcohol or prescription medications
- Consume THC in a safe and comfortable environment with trusted friends or loved ones
- Avoid driving or operating heavy machinery while under the influence
- Be aware of local laws and regulations regarding THC use
- Consider consulting with a healthcare provider or qualified cannabis specialist for guidance on dosage, frequency, and other important factors
- Stay hydrated and well-nourished while using THC, and take breaks as needed to avoid overuse or tolerance development.
THC and Legalization: The Current Status of Cannabis Laws

The legalization of cannabis, including THC-containing products, has been a topic of ongoing debate and discussion in many countries around the world.
Thailand has a long history of cannabis use in traditional medicine, but until recently, its use and possession were strictly prohibited under the country’s Narcotics Act. However, in 2018, Thailand became the first country in Southeast Asia to legalize medical cannabis, allowing for the cultivation, sale, and possession of cannabis for medical purposes.
The law allows patients with certain medical conditions, such as cancer, Parkinson’s disease, and epilepsy, to access medical cannabis with a prescription from a licensed healthcare provider. In addition, the law permits Thai citizens to cultivate up to six cannabis plants for personal medical use, with the requirement to register with the government and obtain a permit.
The legalization of medical cannabis in Thailand has been seen as a significant step forward in recognizing the potential health benefits of cannabis and promoting access to safe and effective medical treatments. However, recreational cannabis use and possession remains illegal in Thailand and can result in severe legal penalties.
The History of Cannabis Prohibition and Its Impact on Society
Cannabis prohibition has a long and complex history, shaped by factors such as politics, racism, and public health concerns.
The origins of cannabis prohibition can be traced back to the early 20th century, when countries such as the United States and Canada began to criminalize the use and possession of cannabis due to concerns over its perceived association with crime and immorality. In the 1930s, the US government led a campaign against cannabis use, fueled by propaganda films such as “Reefer Madness” and the racialized fear of Mexican and Black communities who were seen as using cannabis.
Over time, cannabis prohibition spread to other countries around the world, with many adopting strict criminal penalties for its use and possession. However, the impact of cannabis prohibition has been controversial and widely debated. Critics argue that prohibition has led to the disproportionate criminalization of marginalized communities, including people of color and low-income individuals, and has contributed to the growth of organized crime and violence. In addition, the criminalization of cannabis has hindered research into its potential medical benefits and limited access to safe and regulated cannabis products for those who could benefit from them.
In recent years, there has been a growing movement to reform cannabis laws, with many countries legalizing cannabis for medical or recreational use, and others decriminalizing or reducing penalties for possession. Supporters of cannabis legalization argue that it can promote public health, reduce crime and violence, and generate tax revenue for governments. However, opponents continue to express concerns about the potential risks of cannabis use, including addiction, impaired driving, and mental health issues. The ongoing debate over cannabis prohibition and legalization highlights the complex and multifaceted nature of drug policy and the need for evidence-based approaches that prioritize public health and social justice.
The Legalization Movement: Where Cannabis Is Legal and What It Means
The legalization movement for cannabis has gained momentum in recent years, with many countries and states around the world relaxing their laws on cannabis use and possession. Currently, several countries have legalized cannabis for both medical and recreational use, including Canada, Uruguay, and several states in the United States. In addition, many other countries have decriminalized cannabis possession or have legalized it for medical use only.
The legalization of cannabis has significant implications for public policy, public health, and the economy. Proponents argue that legalization can reduce crime and violence associated with the black market for cannabis, generate tax revenue for governments, and provide safe and regulated access to cannabis products for those who could benefit from them. Legalization has also been seen as a way to address social justice issues, particularly the disproportionate impact of cannabis prohibition on marginalized communities.
However, opponents of legalization express concerns about the potential risks of cannabis use, particularly the risk of addiction, impaired driving, and mental health issues. There are also concerns about the impact of legalization on youth use and access to cannabis, as well as the potential for cannabis to be a gateway drug to other illicit substances.
As the legalization movement continues to gain traction, it is likely that more countries and states will consider legalizing or decriminalizing cannabis in the coming years. However, the debate over the risks and benefits of cannabis use and legalization is likely to continue, and will require careful consideration of the evidence and ongoing monitoring of the impacts of policy changes on public health and safety.
Challenges and Controversies Surrounding THC Legalization: Public Perception, Social Equity, and Business Regulations
The legalization of THC has been accompanied by various challenges and controversies, particularly around public perception, social equity, and business regulations.
Public perception of THC legalization remains a contentious issue, with many people still harboring negative stereotypes and misconceptions about cannabis use. This has made it difficult to shift public opinion towards supporting legalization and promoting a more informed and nuanced understanding of the risks and benefits of cannabis use.
Social equity is another key concern surrounding THC legalization. In many cases, marginalized communities that were disproportionately affected by cannabis prohibition have been left out of the legal cannabis industry, and may continue to face criminalization for cannabis-related offenses. There are also concerns about the impact of legalization on youth use and access to cannabis, particularly in communities where there may be limited resources for drug education and prevention.
Business regulations are also a complex issue in the context of THC legalization. While legalization has opened up new economic opportunities in the cannabis industry, there are challenges around ensuring that the industry is regulated in a way that promotes safety, quality control, and equitable access. Some argue that business regulations have been overly restrictive and have favored large corporations over smaller businesses and marginalized communities.
THC Products and Consumption Methods: Exploring the Options

THC Edibles: How They Work and What to Watch Out For
THC edibles are a popular way to consume cannabis, but they can also be one of the riskiest methods if not used carefully. Edibles come in a variety of forms, from gummies to baked goods, and are made by infusing the product with cannabis extract or cannabis butter. When ingested, the THC is metabolized in the liver, producing a more potent and longer-lasting high than smoking or vaporizing.
THC Tinctures and Oils: How to Use Them Safely and Effectively
THC tinctures and oils are concentrated liquid forms of cannabis extract that can be ingested orally or added to food or beverages. They are typically made by soaking cannabis flowers in high-proof alcohol or glycerin to extract the cannabinoids and terpenes, resulting in a potent and fast-acting product.
When using THC tinctures and oils, it’s important to start with a low dose and wait at least an hour before consuming more. The effects of tinctures and oils can be felt within 15 to 45 minutes of ingestion, making it easier to monitor the dosage and avoid overconsumption.
Smoking and Vaping THC: Pros and Cons of Different Devices and Techniques
When smoking THC, the most common method is using a joint or a blunt, which involves rolling cannabis into paper or a tobacco leaf. Other smoking devices include pipes, bongs, and bubblers. The benefits of smoking THC include the immediate onset of effects and the ability to easily control the dosage. However, smoking can also have negative health effects such as respiratory issues and exposure to harmful chemicals produced by combustion.
Vaping THC involves heating cannabis oil or flowers at a lower temperature than smoking, which creates a vapor that can be inhaled. Vaping can be done with a variety of devices, including vape pens and tabletop vaporizers. The benefits of vaping include a more controlled temperature and the ability to customize the flavor and potency of the product. However, there are concerns about the safety of vaping due to the potential for harmful chemicals to be released when heating the cannabis oil or flower.
The Addictive Potential of THC: Is Cannabis Really Addictive?
While cannabis use may not be as physically addictive as some other drugs, such as opioids, it can still be habit-forming and lead to psychological dependence. The addictive potential of THC largely depends on factors such as frequency and dosage of use, as well as individual susceptibility.
Studies have found that regular cannabis use can lead to changes in the brain’s reward and motivation pathways, which may contribute to addiction. Additionally, withdrawal symptoms such as irritability, anxiety, and sleep disturbances can occur when heavy cannabis users try to quit, further highlighting the addictive potential of THC.
It’s important to note that not everyone who uses cannabis will develop an addiction, and many people are able to use THC products without issue. However, for those who do develop problematic use, there are treatment options available such as therapy and medication-assisted treatment.
Defining Addiction and Substance Use Disorder
THC addiction, also known as cannabis addiction, refers to a pattern of problematic use of THC-containing products that leads to significant impairment or distress in the user’s life. It is characterized by a persistent desire to use cannabis despite negative consequences, difficulty controlling or reducing use, and withdrawal symptoms when use is stopped or reduced.
Substance use disorder (SUD) is a broader term that encompasses addiction to various substances, including THC. It is diagnosed when an individual’s use of a substance such as cannabis leads to significant impairment or distress in their life, and is characterized by a pattern of problematic use that includes at least two of the following criteria within a 12-month period:
- Using the substance in larger amounts or for longer periods than intended
- Difficulty controlling or reducing substance use
- Spending a lot of time obtaining, using, or recovering from substance use
- Craving or a strong desire to use the substance
- Failure to fulfill major obligations at work, school, or home due to substance use
- Continuing to use the substance despite knowledge of negative consequences
- Giving up important social, occupational, or recreational activities due to substance use
- Using the substance in situations where it is physically hazardous
- Developing tolerance to the substance
- Experiencing withdrawal symptoms when use is stopped or reduced.
A diagnosis of SUD can range from mild to severe, depending on the number of criteria met. Treatment for THC addiction and SUD can involve a combination of therapy, medication-assisted treatment, and support groups.
The Debate over Cannabis Addiction: Controversies and Misconceptions
The debate over cannabis addiction is a controversial topic that has led to many misconceptions and debates. One of the biggest controversies surrounding cannabis addiction is whether or not it is a real addiction. Some people argue that cannabis addiction is not a genuine addiction, as it lacks the physical withdrawal symptoms that are often associated with other drugs like opioids or alcohol.
However, research suggests that cannabis addiction is a real phenomenon that can lead to significant problems for individuals who struggle with it. For example, studies have shown that individuals who use cannabis regularly can experience withdrawal symptoms such as irritability, anxiety, and sleep disturbances when they try to quit. Additionally, research has linked cannabis addiction to negative outcomes such as impaired cognitive function, decreased motivation, and mental health problems.
Another misconception surrounding cannabis addiction is that it is not as harmful as other types of addiction. While it is true that cannabis addiction may not have the same physical health consequences as other types of addiction, it can still have significant negative impacts on an individual’s life. For example, it can lead to problems with relationships, work, and legal issues.
Understanding Cannabis Use Disorder: Symptoms, Risk Factors, and Treatment Options

Cannabis Use Disorder (CUD) is a condition where an individual experiences problematic patterns of cannabis use that lead to significant impairment or distress.
The Diagnostic Criteria for Cannabis Use Disorder
According to the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), the diagnostic criteria for cannabis use disorder include a problematic pattern of cannabis use that leads to clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. To receive a diagnosis of cannabis use disorder, an individual must meet at least two of the following criteria within a 12-month period:
Common Symptoms of Cannabis Use Disorder
Cannabis Use Disorder (CUD) is a condition where an individual experiences problematic patterns of cannabis use that lead to significant impairment or distress. CUD is characterized by several symptoms, including:
- Using more cannabis than intended, or using it for longer than intended.
- Difficulty cutting down or controlling cannabis use.
- Spending a lot of time using cannabis or recovering from its effects.
- Strong cravings or urges to use cannabis.
- Failing to fulfill obligations at work, school, or home because of cannabis use.
- Continuing to use cannabis despite persistent social or interpersonal problems caused by its use.
- Giving up important activities or hobbies because of cannabis use.
- Using cannabis in situations where it is physically hazardous.
- Continuing to use cannabis despite knowledge of its negative physical or psychological effects.
- Developing tolerance, which means that more cannabis is needed to achieve the desired effect.
- Experiencing withdrawal symptoms when reducing or stopping cannabis use.
The risk factors for developing CUD include starting cannabis use at a young age, using
cannabis frequently, and having a family history of substance use disorders.
Risk Factors for Cannabis Addiction and Dependence
There are several factors that can increase the risk of developing cannabis addiction and dependence. These include:
- Genetics: Some people may have a genetic predisposition to addiction, which can increase the likelihood of developing cannabis use disorder.
- Early onset of use: Using cannabis at a young age, particularly before the age of 18, can increase the risk of developing addiction later in life.
- Frequency and amount of use: People who use cannabis frequently and in large amounts are more likely to develop dependence and addiction.
- Mental health issues: People with mental health issues, such as depression, anxiety, or PTSD, are more likely to use cannabis to self-medicate, which can lead to addiction.
- Environmental factors: Living in an environment where cannabis use is common or socially acceptable can increase the likelihood of developing addiction.
- Personal factors: Other personal factors, such as stress, trauma, or lack of social support, can also increase the risk of developing cannabis addiction and dependence.
Treatment Options for Cannabis Use Disorder: Therapy, Medications, and Support Groups
The treatment options for cannabis use disorder typically involve a combination of therapy, medications, and support groups. Behavioral therapies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and motivational enhancement therapy (MET) are commonly used to treat cannabis addiction. These therapies aim to help individuals recognize and change their problematic behaviors, beliefs, and thought patterns related to cannabis use.
In addition to therapy, some medications have shown promise in treating cannabis use disorder. For example, the medication dronabinol, which is a synthetic form of THC, has been used to reduce cannabis withdrawal symptoms. Other medications such as naltrexone and gabapentin may also be used to treat cannabis addiction.
Support groups such as Marijuana Anonymous (MA) can also be helpful for individuals seeking to overcome cannabis addiction. These groups provide a safe and supportive environment where individuals can share their experiences, receive guidance and encouragement, and learn from others who have gone through similar struggles.
THC Withdrawal: What Happens When You Stop Using Cannabis?
When someone stops using THC after regular or heavy use, they may experience withdrawal symptoms. The severity and duration of these symptoms can vary depending on factors such as frequency and duration of use, dosage, and individual differences in metabolism.
Common Symptoms of THC Withdrawal: Irritability, Insomnia, and Appetite Changes
When a person stops using THC, they may experience a range of withdrawal symptoms, including:
- Irritability: This is a common symptom of THC withdrawal, and it can lead to feelings of frustration and anger.
- Insomnia: Many people who stop using THC experience difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep. This can lead to fatigue, daytime sleepiness, and impaired cognitive function.
- Appetite changes: THC use can affect a person’s appetite, and withdrawal from THC can lead to changes in appetite, including decreased appetite or increased appetite.
- Mood changes: THC withdrawal can also cause changes in mood, including anxiety, depression, and restlessness.
- Physical symptoms: Some people may experience physical symptoms such as headaches, sweating, and nausea during THC withdrawal.
The Duration and Severity of THC Withdrawal: How Long Does It Last and What Factors Affect It?
The duration and severity of THC withdrawal can vary depending on several factors such as the frequency and amount of THC use, individual differences in metabolism, and other health factors. In general, withdrawal symptoms may start within a few days to a week after discontinuing THC use and can last for several weeks or more.
The severity of THC withdrawal can also vary depending on the individual, with some people experiencing only mild symptoms while others may experience more severe symptoms. The most common symptoms of THC withdrawal include irritability, insomnia, anxiety, depression, and changes in appetite.
Other factors that may affect the duration and severity of THC withdrawal include the method of consumption (e.g., smoking, vaping, edibles), co-occurring mental health conditions, and any previous history of substance abuse.
Coping Strategies and Treatment Options for THC Withdrawal: Self-Care, Therapy, and Medications
There are several coping strategies and treatment options available for managing THC withdrawal symptoms. Here are some options to consider:
- Self-care: Practicing good self-care habits can help ease some of the symptoms of THC withdrawal. This can include getting enough sleep, eating a healthy and balanced diet, staying hydrated, and engaging in regular exercise or physical activity.
- Therapy: Therapy can be a helpful tool for managing THC withdrawal symptoms. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is one type of therapy that has been found to be effective in helping people overcome substance use disorders, including cannabis addiction.
- Medications: In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help manage the symptoms of THC withdrawal. For example, medications such as antidepressants or anti-anxiety drugs may be used to treat mood disorders that can arise during withdrawal.
It’s important to note that withdrawal symptoms can vary in severity and duration, depending on several factors such as the frequency and amount of THC use, age, and overall health. It’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best course of action for managing THC withdrawal symptoms.

Summarize
THC is a psychoactive compound found in cannabis that interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system to produce a range of effects, including pain relief, appetite stimulation, and mood alteration. While THC can offer numerous health benefits, it also poses risks and side effects, particularly with long-term or heavy use. To use THC safely and responsibly, it is important to understand proper dosage, consumption methods, and potential risks. Additionally, THC addiction and withdrawal are real concerns, and treatment options are available for those struggling with cannabis use disorder. As cannabis legalization continues to expand, it is essential to stay informed about the current status of cannabis laws, as well as the controversies and challenges surrounding THC use and legalization.











 @bloom.asia
@bloom.asia




